The logical parsing mode is used to construct logical expressions.
To construct these logical expressions, you can combine different elements, such as field codes, JWT expression parser functions and operators. The result must always return one of two distinct BOOLEANvalues:
true
or
false.
The main JWT features where you will be using the logical parsing mode are:
- Conditional execution
- Logical condition
- Logical validator
- Boolean condition
- JWT JQL functions
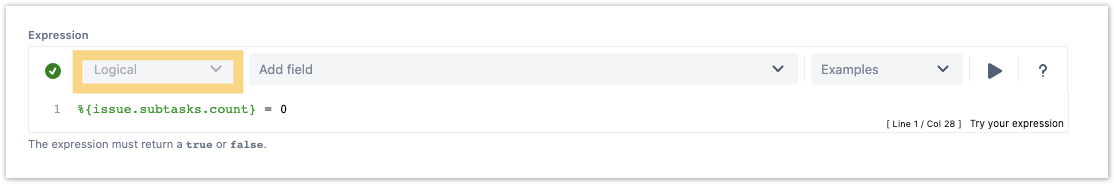
 Example expressions
Example expressions
| Parser expression | Description |
|---|---|
3 < 5 | This example returns:
|
3 > 5 | This example returns:
|
Expressions can be combined or linked using operators to construct complex logical comparisons.
| Parser expression | Description |
|---|---|
3 < 5 AND 7 > 5 | This example returns:
|
%{issue.assignee} = %{issue.reporter}
| This example returns:
|
| Parser expression | Description |
|---|---|
false | Simply returns false. You can use this expression for "switching off" a specific post function. |
{parent.votes} > 5
| A numerical comparison which returns true if the parent issue has more than 5 votes. |
%{issue.assignee} = %{issue.project.lead} and %{issue.issueType} = "Bug"
(%{issue.assignee} = %{issue.project.lead}) and (%{issue.issueType} = "Bug")
| A logical conjunction which takes two comparisons as operands. It returns true when the assignee of the issue is the project lead and if it's a Bug. The second expression has the same meaning but due to use of brackets may be more readable. |
%{issue.assignee} = null
| Returns true if the issue does not have an assignee. This expression uses the null value as an operator. |
%{issue.priority} IN ["Blocker", "Critical"]
%{issue.priority} = "Blocker" OR %{issue.priority} = "Critical"
| Returns true if the Priority has the value "Blocker" or "Critical". The first expressions uses a list whereas the second one uses single comparisons connected via the logical operator OR. |
%{issue.issueType} = "Bug" IMPLIES %{issue.versions} != null
| Returns true if Affects version/s is set whenever the issue type equals "Bug". |
%{issue.priority} IN ["Blocker", "Critical", "Major"] IMPLIES (%{issue.assignee} != null AND %{issue.duedate} != null)
| Returns true if Priority is "Blocker", "Critical" or "Major", the issue is assigned and Due date is set. |
%{issue.labels} ~ ["Blocker", "Critical", "Major"]
| Returns true if Labels (which is a field holding a TEXT LIST) contains "Blocker", "Critical" or "Major". |
The operators, their meaning and the applicable data types you can use them with are listed below. A comparison always returns a BOOLEAN value. All operators respect the case of the characters. When working with Lists, each elements' existence and its order are being evaluated. When working with Lists, each elements' existence and its order are being evaluated. When comparing lists, the exact number of occurence (cardinality) per element must match. The following comparison operators can be used with TEXT and TEXT LIST data types . All operators ignore the case of the characters. Below you find a comprehensive matrix of all operators and applicable data types . BOOLEAN NUMBER TEXT NUMBER LIST TEXT LIST ISSUE LIST Please be aware the both operands of the respective comparison must have the same data type. The only exceptions are the following: Operators Operators The table below lists all logical operators that can be used for linking logical terms in an expression. Logical operators take logical terms (which return BOOLEAN values) as operands and can thus be built using: Logical operators can only be used in logical expressions in the Logical mode or in combination with the conditional operator. Operator Meaning Precedence A single logical term can be enclosed by brackets () in order to increase the readability of the expressions or to define a precedence which differs from the given one. Logical operators can also be written in lower case (e.g. The conditional operator It basically allows you to construct the following expression: IF logical_expression The conditional operator is extremely helpful when being used in calculated fields. IF the priority of an issue is Blocker, THEN this function will return "Please have a look at this issue immediately" ELSE it will return "No stress, come back later". IF an issue does have a due date set (due date is not null), THEN this function will return the number of hours from the current date-time to the due date ELSE it will return IF a custom field (e.g. a select list) has a value of Red, THEN this function will return "Color", ELSE it will return "No color". IF the current time is between 21:00 and 7:00 THEN this function will return "Night" , ELSE it will return "Day".![]() Comparison operators
Comparison operatorsOperator Meaning Examples (all examples return true)
=
equal to 1=1
true = true
[1, 2, 3] = [1, 2, 3]
["blue", "red", "green"] = ["blue", "red", "green"]
!=
not equal to 0 != 1
"HELLO" != "Hello"
%{issue.description} != "Hello"
true != false
[1, 2, 3] != [1, 3, 2]
["blue", "red", "green"] != ["blue", "green", "red"]
<
less than 1 < 2
"abc" < "bbc"
"abc" < "abcd"
>
greater than 2 > 1
"bbc" > "abc"
"abcd" > "abc"
<=
less than or equal to 3 <= 3
>=
greater than or equal to "Hello world! Hello *" >= "Hello world"
~
contains "Hello world!" ~ "world" #true. The text "world" is contained in the first text.
%{issue.components.leads} ~ %{system.currentUser} #checks whether "Component leads" contains the "Current user".
[1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 4] ~ [2, 1, 2] #true
["blue", "red", "green", "red", "white", "red"] ~ ["red", "green", "red"] #true
["green", "red"] ~ ["red", "green", "red"] #false
!~
does not contain "Hello world!" !~ "world" #false. The text "world" is contained in the first text.
%{issue.fixVersions} !~ %{issue.versions} #false if all "Affects version/s" are also selected as "Fix version/s".
[1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 4] !~ [2, 1, 1, 4] #true
["blue", "red", "green", "red", "red"] !~ ["red", "green", "green", "red"] #true
in
is contained in "world" in "Hello world!" #true. The text "world" is contained in the first text.
%{system.currentUser} in %{issue.components.leads} #true if current user is a component lead of any of the issue's components
[1, 1, 2] in [2, 1, 1, 1, 4] #true
["blue", "red", "red"] in ["red", "green", "blue", "red", "red"] #true
2 in [1, 2, 3] #true
"blue" in ["red, "blue", "white"] #true
not in
is not contained in "Hello world!" not in "world" #true
%{issue.versions} not in %{issue.fixVersions} #false if all "Affects version/s" are also selected as "Fix version/s".
[1, 1, 2, 2] not in [2, 1, 1, 1, 4] #true
["blue", "red", "red", "blue"] not in ["red", "blue", "red", "red"] #true
5 not in [1, 2, 3, 3, 4] #true
"orange" not in ["blue", "red", "white"] #true
any in
any element is in %{issue.versions} any in %{issue.fixVersions} # true if any selected "Affects version/s" has also been selected as "Fix version/s".
[1, 3] any in [3, 4, 5] #true
["blue", "white"] any in ["black", "white", "green"] #true
none in
no single element is in %{issue.versions} none in %{issue.fixVersions} #true if no selected "Affects version/s" has also been selected as "Fix version/s".
[1, 2] none in [3, 4, 5] #true
["blue", "red"] none in ["black", "white", "green"] #true
Parser expression Output Description ["blue", "red", "green", "red", "white", "red"] ~ ["red", "green", "red"]
true This expression returns
true
, since the element (text) red appears at least twice in the first list and the element (text) green occurs at least once in the first list.["green", "red"] ~ ["red", "green", "red"]
false This expression returns
false
, since the element (text) red does not appear twice in the first list. Operator Meaning Examples (all examples return true)
=~
equal to
"HELLO" =~ "Hello" #true
"up" =~ "UP" #true
["blue", "red", "green"] =~ ["Blue", "RED", "Green"] #true
!=~
not equal to
" HELLO" !=~ "Hello" #false, since there is a whitespace in the first text
"up" !=~ "down" #true
("up" !=~ "UP") #false
["blue", "red"] !=~ ["Blue", "green"] #true
["blue", "red"] !=~ ["Red", "BLUE"] #true
["blue", "red", "green"] !=~ ["Blue", "RED", "Green"] #false
~~
contains
"Hello World!" ~~ "world" #true, checks whether a text contains a substring.
"A small step for a man" ~~ "STEP" #true
["one", "two", "three"] ~~ ["TWO", "One"] #true, checks whether a text list contains all the elements of another text list.
!~~
does not contain
"Hello World!" !~~ "bye" #true, checks whether a text does not contain a substring.
"A small step for a man" !~~ "big" #true
["one", "two", "three"] !~~ ["Four"] #true, checks whether a text list does not contain a single element of another text list.
(["one", "two", "three"] !~~ ["TWO"]) = false
in~
is contained in
"world" in~ "Hello World!" #true, checks whether a substring is contained in another text.
"STEP" in~ "A small step for a man" #true
["TWO", "One"] in~ ["one", "two", "three"] #true, checks whether all the elements of a text list are contained in another text list.
not in~
is not contained in
"bye" not in~ "Hello World!" #true, checks whether a substring is not contained in another text.
"big" not in~ "A small step for a man" #true
["Four"] not in~ ["one", "two", "three"] #true, checks whether any of the elements of a text list are not contained in another text list.
["TWO"] not in~ ["one", "two", "three"] #false
any in~
any element is in
["blue", "violet"] any in~ ["Blue", "Red", "Green"] #true
["Five", "One"] any in~ ["FOUR", "FIVE", "SIX"]"bye" #true
none in~
no single element is in
["Orange"] none in~ ["red", "blue", "green"] #true, checks whether none of the elements of a text list are not contained in another text list.
["orange"] none in~ ["Red", "Orange"] #false
Comparison Operator
=
!=
<
- - - -
>
- - - -
<=
- - - -
>=
- - - -
~
- -
!~
- -
in
- -
not in
- -
any in
- - -
none in
- - -
=~
- - - -
!=~
- - - -
~~
- - - -
!~~
- - - -
in~
- - - -
not in~
- - - -
any in~
- - - - -
none in~
- - - - -
~, !~, in
and
not in
can be used for checking a single element (NUMBER or TEXT) against a NUMBER LIST or a TEXT LIST
null
.Remember Examples
~, !~, in
and
not in
can be used for checking a single element (NUMBER or TEXT) against a NUMBER LIST or a TEXT LIST 1 in [1, 2, 3]
["blue", "red"] ~ "blue"
Operators
~, !~, in
and
not in
when used with a text are useful to look for substrings in another string."I love coding" ~ "love"
"I don't like Mondays" !~ "Fridays"
"love" in "I love coding"
"Fridays" not in "I don't like Mondays"
Operators
~, !~, in
and
not in
respect cardinality, i.e., container list must have at least the same number of elements as contained list.[1, 1] in [1, 1, 1]
[1, 1] not in [1, 2, 3]
Operators
=
and
!=
, when used for comparing lists, require to have the same elements, with the same cardinality and the same order.[1, 2, 3] = [1, 2, 3]
[4, 5, 6] != [4, 6, 5]
<, >, <=
and
>=
work according to lexicographical order when comparing text.1 < 2
"abc" < "bbc"
"abcd" > "abc"
![]() Logical operators
Logical operators NOT or
!
logical negation 1 (highest)
AND
or
&
logical conjunction 2
OR
or
|
logical disjunction 3
XOR
exclusive or, i.e.,
a XOR b
is equivalent to
a AND !b OR !a AND b
3 IMPLIES or
IMP
logical implication, i.e.,
a IMPLIES b
is equivalent to
!a OR b
4
XNOR
or
EQV
logical equivalence, i.e.,
a EQV b
is equivalent to
a IMPLIES b AND b IMPLIES a
4 (lowest)
and
,
or
)![]() Conditional operator
Conditional operator
?
:
is a powerful operator to construct conditional expressions.true THEN term_1 ELSE term_2.<logical_expression> ? <term_1> : <term_2>
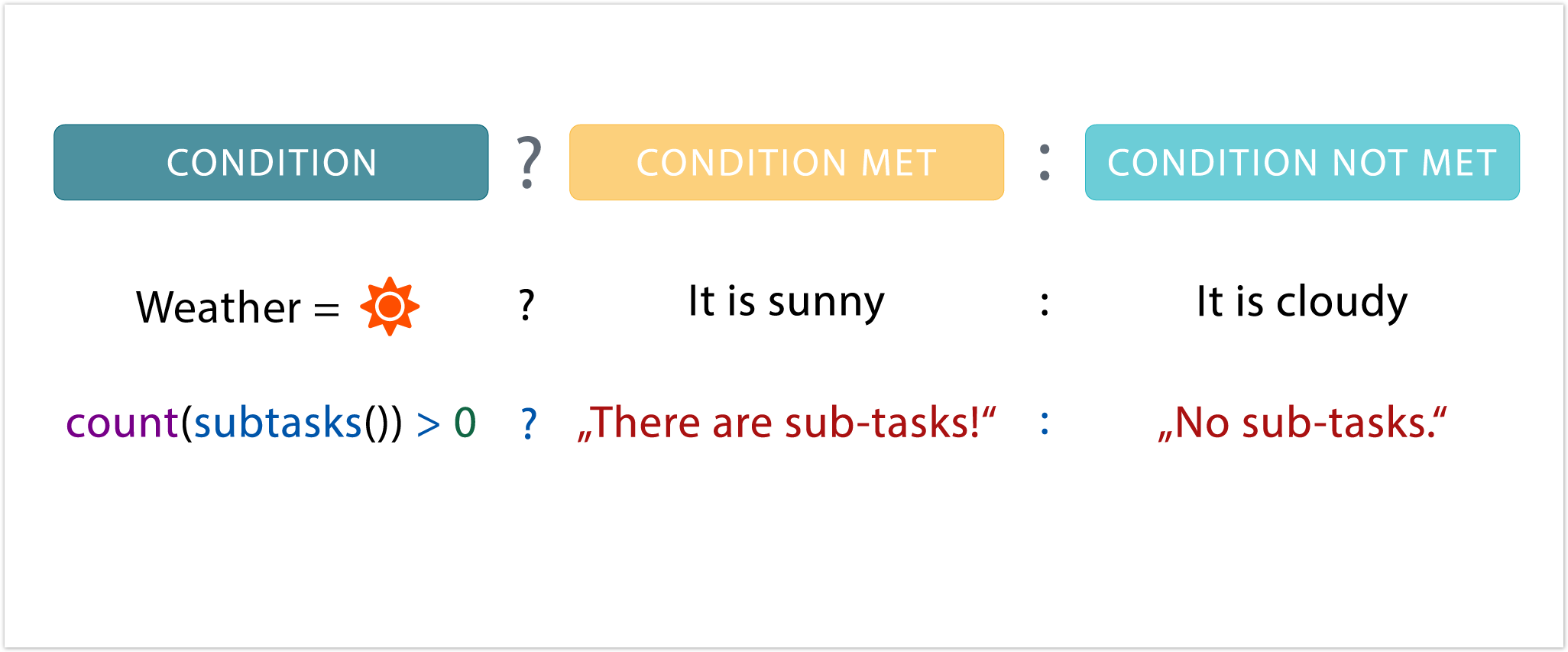
Expression Description %{issue.priority} = "Highest" ? "Please have a look at this issue immediately" : "No stress, come back later"
{issue.duedate} != null ? ({...duedate} - {...currentDateTime}) / {HOUR} : 0
0
.%{issue.somefield} = "Red" ? "Color" : "No color"
timePart({...currentDateTime}, LOCAL) > 21:00 AND timePart({...currentDateTime}, LOCAL) < 7:00 ? "Night" : "Day"
If you still have questions, feel free to refer to our support team.